this post was submitted on 28 Oct 2024
815 points (98.7% liked)
Science Memes
11972 readers
2073 users here now
Welcome to c/science_memes @ Mander.xyz!
A place for majestic STEMLORD peacocking, as well as memes about the realities of working in a lab.

Rules
- Don't throw mud. Behave like an intellectual and remember the human.
- Keep it rooted (on topic).
- No spam.
- Infographics welcome, get schooled.
This is a science community. We use the Dawkins definition of meme.
Research Committee
Other Mander Communities
Science and Research
Biology and Life Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !reptiles and [email protected]
Physical Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Humanities and Social Sciences
Practical and Applied Sciences
- !exercise-and [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !self [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Memes
Miscellaneous
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
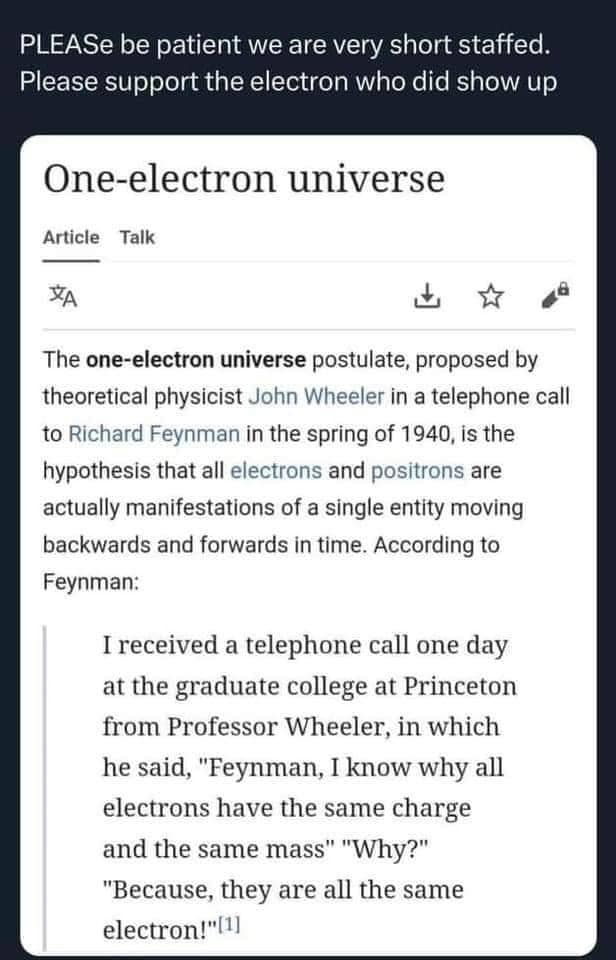
The whole thing is an abstraction. The nucleus isn't actually tiny ball shaped things mashed together, but rather cloudy stuff which would probably not be identical if we could actually see them. The quarks that make up protons and neutrons are considered elementary particles and identical, but they don't move around much unless energy is used to split them.
The electron however is an elementary particle that moves outside of the nucleus and can move from one atom to another. So the hypothesis is that if we could follow one electron from the big bang to the end of the universe, and this electron could move both forwards and backwards in time, it would potentially be enough with just one.
It probably doesn't hold up very well, but it's an interesting thought experiment.
It's one of those things which would be pretty much impossible to prove, but it holds well with the effects we currently see. Electrons can annihilate by colliding with positrons. But the collision we see could be a single electron changing from moving forwards in time to moving backwards in time. It holds that it's the same particle in the equations by cancelling out the minus sign of the charge with the minus sign in the time. So while we see a collision, the electron would just see itself changing charge and start moving backwards in time instead.
It's a beautiful hypothesis, and fills me with chills to think about the electron "experiencing" all of history an unimmaginable amount of times.