this post was submitted on 06 Jul 2023
13 points (93.3% liked)
Superstonk
798 readers
1 users here now
Reddit was down... So I made a Superstonk alternative in Lemmy.
founded 3 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
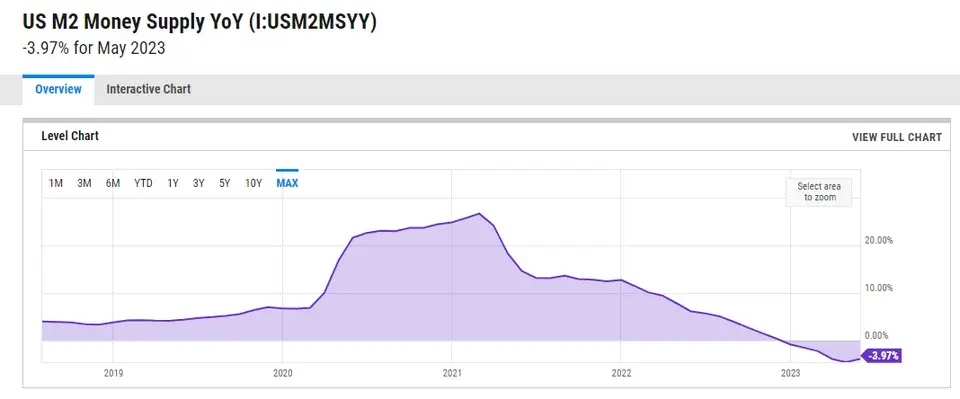
Stupid question: what does this mean?
I didn't know either, so I asked GPT.
A decreasing year-over-year (YoY) USD M2 money supply can have several implications for the economy and financial markets. Here are some potential effects:
Tightening Monetary Conditions: A declining M2 money supply suggests a reduction in the amount of money circulating in the economy. This can indicate a tightening of monetary conditions as the central bank may be implementing policies to curb inflation or control excessive money growth. It could involve measures such as reducing money creation, increasing interest rates, or implementing other monetary policy tools.
Reduced Liquidity: A decrease in the M2 money supply implies a decrease in the overall liquidity available in the economy. This can affect borrowing and lending activities, as there may be less money available for banks to lend to businesses and individuals. Reduced liquidity can have a dampening effect on economic growth and investment.
Impact on Interest Rates: A declining M2 money supply can put upward pressure on interest rates. With less money available in the system, lenders may demand higher interest rates to compensate for the reduced availability of funds. This can affect borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially slowing down borrowing and spending activities.
Potential Impact on Asset Prices: A decrease in the money supply can influence asset prices in financial markets. With less money available for investment, investors may find it harder to access funds for buying assets such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. This can potentially lead to a decrease in asset prices if demand weakens.
Impact on Inflation: A declining M2 money supply can act as a disinflationary or deflationary factor. With less money in circulation, there may be reduced pressure on prices, leading to lower inflationary expectations. However, the impact on inflation would depend on various other factors such as the overall economic conditions, fiscal policies, and supply-demand dynamics.
It's important to note that changes in the money supply alone may not fully capture the complexity of economic dynamics. The implications of a decreasing M2 money supply should be considered in conjunction with other economic indicators, policy actions, and broader market conditions to assess the overall impact on the economy.