this post was submitted on 17 Oct 2024
1232 points (98.6% liked)
Science Memes
11217 readers
2393 users here now
Welcome to c/science_memes @ Mander.xyz!
A place for majestic STEMLORD peacocking, as well as memes about the realities of working in a lab.

Rules
- Don't throw mud. Behave like an intellectual and remember the human.
- Keep it rooted (on topic).
- No spam.
- Infographics welcome, get schooled.
This is a science community. We use the Dawkins definition of meme.
Research Committee
Other Mander Communities
Science and Research
Biology and Life Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !reptiles and [email protected]
Physical Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Humanities and Social Sciences
Practical and Applied Sciences
- !exercise-and [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !self [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Memes
Miscellaneous
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
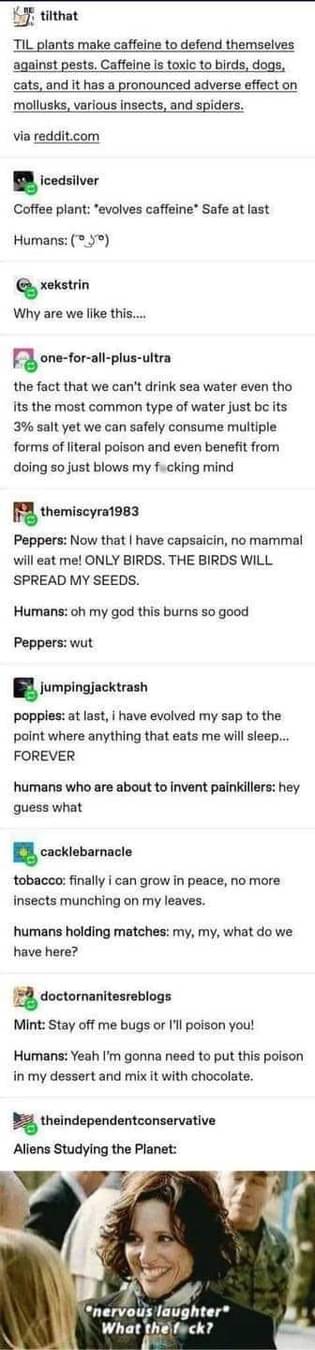
For mammals we are, sure, but there's loads of things that'd kill humans that other animals chow down on perfectly happily, especially when it comes to microorganisms, mushrooms and the rotting things they're often found in/around
I don't think scavenging is right also given that humans used to mainly pick fresh fruits and persistence hunt, both of which are very fresh food which is not overlooked or left by others... Given the fact we picked fresh fruits and hunted for fresh meat, being resistant to berry and fruit based poisons was more important than microorganism based ones, so it makes a lot of sense that so many of the non-intoxicating poisons we like are from fruits and berries
Scavenging carcasses and chasing predators away from a kill is definitely a behavior we had in the past. Particularly during droughts and famines, scavenging would be an important food source on the Saharan scrubland. IIRC, this would've been before persistence hunting was a thing, back in the H.erectus days, maybe even as far back as some Australopiths.
We would also scavenge fallen fruits and berries that were at least partially decayed. It's most likely how we discovered the intoxicating effects of alcohol.