There are many dietary patterns available and in the zeitgeist.
MacroNutrient
On the macronutrient scale we have 3^3 (27) choices, the most common are:
- HCHFLP - High Carb, High Fat, Low Protein : This is the "standard"/default western diet
- HCLFMP - High Carb, Low Fat, Medium Protein: This is the default "healthy" diet recommended by media
- HCLFHP - High Carb, Low Fat, High Protein: A body builder bulking diet
- MCLFHP - Medium Carb, Low Fat, High Protein: Body builder cutting diet
- LCHFMP - Low Carb, High Fat, Moderate Protein : A diet that maintains the metabolic state of ketosis
MicroNutrients
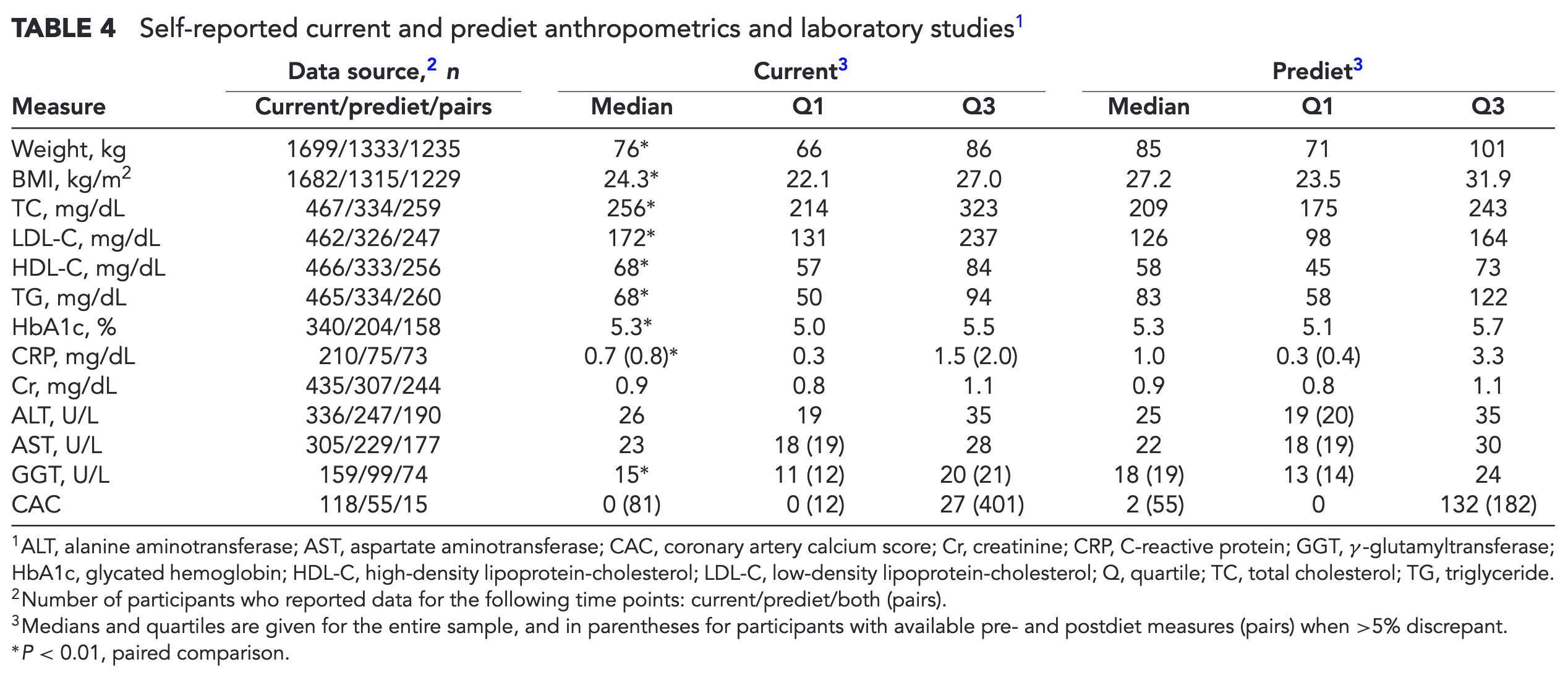
Inside of any macronutrient regime there are essential micronutrients/minerals that are required. Essential means the body does not have the ability to produce them from other sources. There are too many to list here, but using a diet tool like chronometer (free and can use the website) will let you see if your covering your micronutrient targets (Recommend Daily Intakes). One note is that the RDAs are usually minimums (though in some contexts may be more then necessary).
Cronometer example micronutrient display
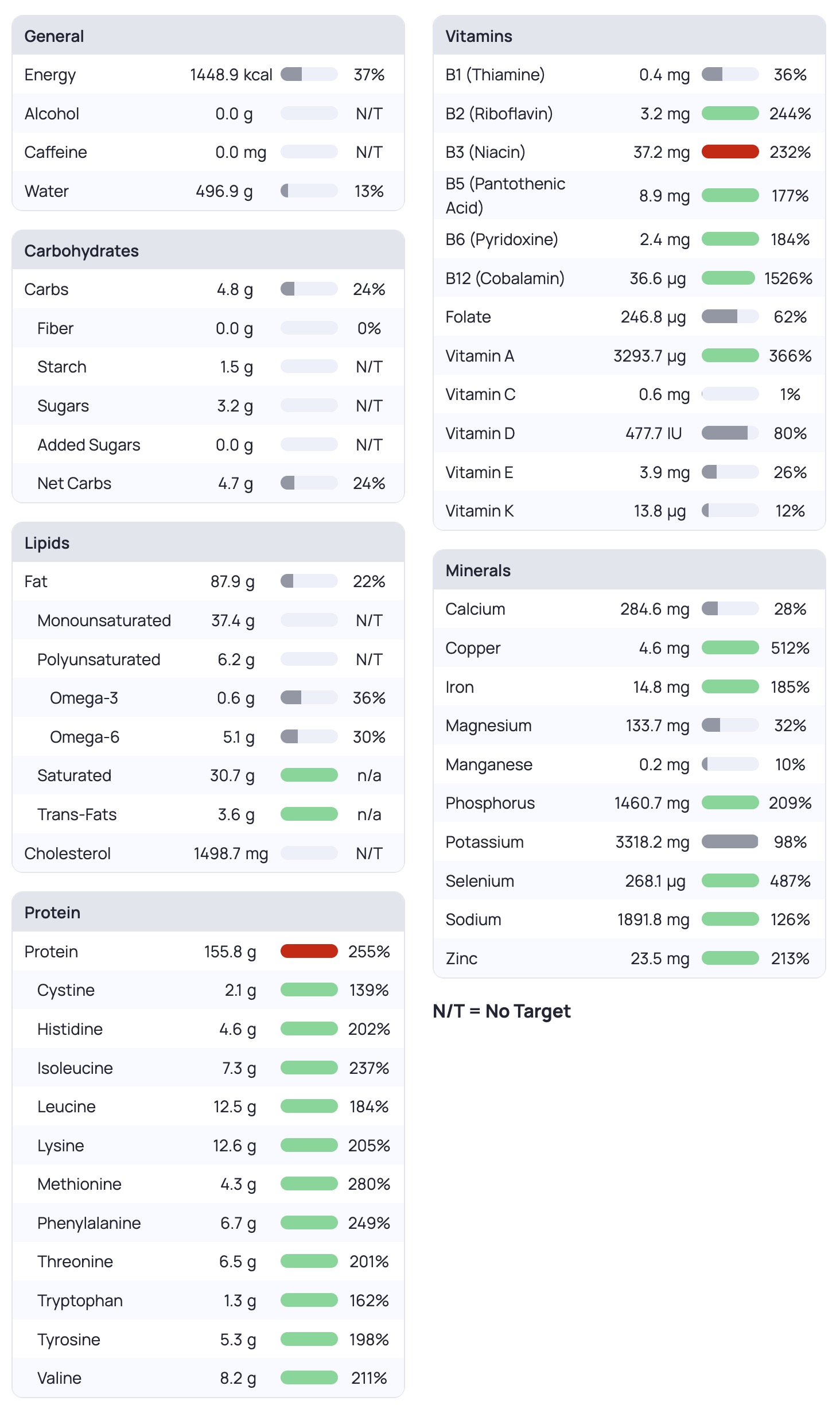
Importantly, VERY importantly, not all foods are ingested by the human body the same, so the amount on the label is not the same that ends up in the body. This is a good paper discussing the bioavailabilty measurements of food, DIAAS seems to be the best scoring system out there to date.
Whole Foods
Regardless of macro and micro nutrient choices, the evidence, and consensus across medical professionals, and zealots, is that eating whole foods from natural sources that are not industrialized and hyper processed is a good guide to health and better outcomes.
If the ingredients for what you are eating are more complex than the name of the thing, you shouldn't eat it. Don't eat food from a factory out of a box and wrapped in plastic!
I.e. shop the outside edge of the grocery store, not the aisles in the middle.
This might be somewhat controversial, but I would include modern seed oils as a type of processed food to be avoided on a Whole food Diet. No vegetable oils that come from a factory please!
Low Carb High Fat / Ketogenic
The LCHF, ketogenic/keto/atkins, macronutrient profile has many benefits - Increasing insulin sensitivity and reducing the issues insulin resistance causes (obesity, hyper tension, pcos, diabetes 2, etc).
The key schism of LCHF diets is over the dietary necessity (or lack thereof) of carbohydrates, this well referenced document is a must read for those who are incredulous. There is NO SUCH THING AS AN ESSENTIAL CARBOHYDRATE - the human body can do gluconeogenesis and produce all the glucose it needs from fat.
Sometimes this LCHF diet is referred to a fed-fasting diet, since it maintains metabolic ketosis even when eating.
The core mechanism of action here is allowing insulin levels to return, and stay at, normal levels throughout the day which enables the body - an amazing homeostasis machine - to function properly. The body is full of feedback mechanisms, like hunger, thirst, satisfaction, etc - to stay in optimal bounds.
Being on a LCHF diet is easy to maintain, because you're not hungry, you can eat as much as you want - you just let your body self regulate.
NOTE - if you are on some medications, such as high blood pressure, and insulin, changing your diet can change the effectiveness of these medications and should be done under medical supervision. Either with your doctor, a metabolic doctor, or a service such as virta. Watch your biomarkers when you change a diet to make sure your medications are not taking you outside of your targets.
LCHF diets can include Plant based diets (vegetarian/vegan), Animal Based Foods (Carnivore), or any mix in between (just keto, or ketovore)
Insulin Sensitivity
93% of Americans (and probably similar in western countries) have insulin resistance, this can manifest as obesity, or high blood pressure, visceral fat, diabetes, etc. It may not be visible at all - Skinny Fat - Thin Outside Fat Inside (TOFI).
You can use your TG/HDL ratio has a very good approximation for your insulin sensitivity. You want to be <0.9 (mmol/L) or <2 (mg/dL). If your ratio is low, congratulations you are insulin sensitive
Carnivore
Carnivore is a strict subset of a LCHF/Ketogenic diet that restricts itself to only animal sourced foods (ASF). The reasons for doing this can include:
- Better food bioavailability - Need to eat less food
- Inflammation from different plant based foods - oxalate / lectins
- Allergies
- Regenerative and Sustainable farming lifestyle (Local farm can provide biocomplete nutrition without needed to transport rare foods over long distances)
- Ease of adherence (not that many choices, hard to do it wrong, don't have to count carbs)
ASFs are almost entirely digested in the stomach and large intestine, very little makes it to the small intestine - This is why people eating strict carnivore have less frequent bowel movements, and people with gut issues can see impactful quality of life improvements on this intervention
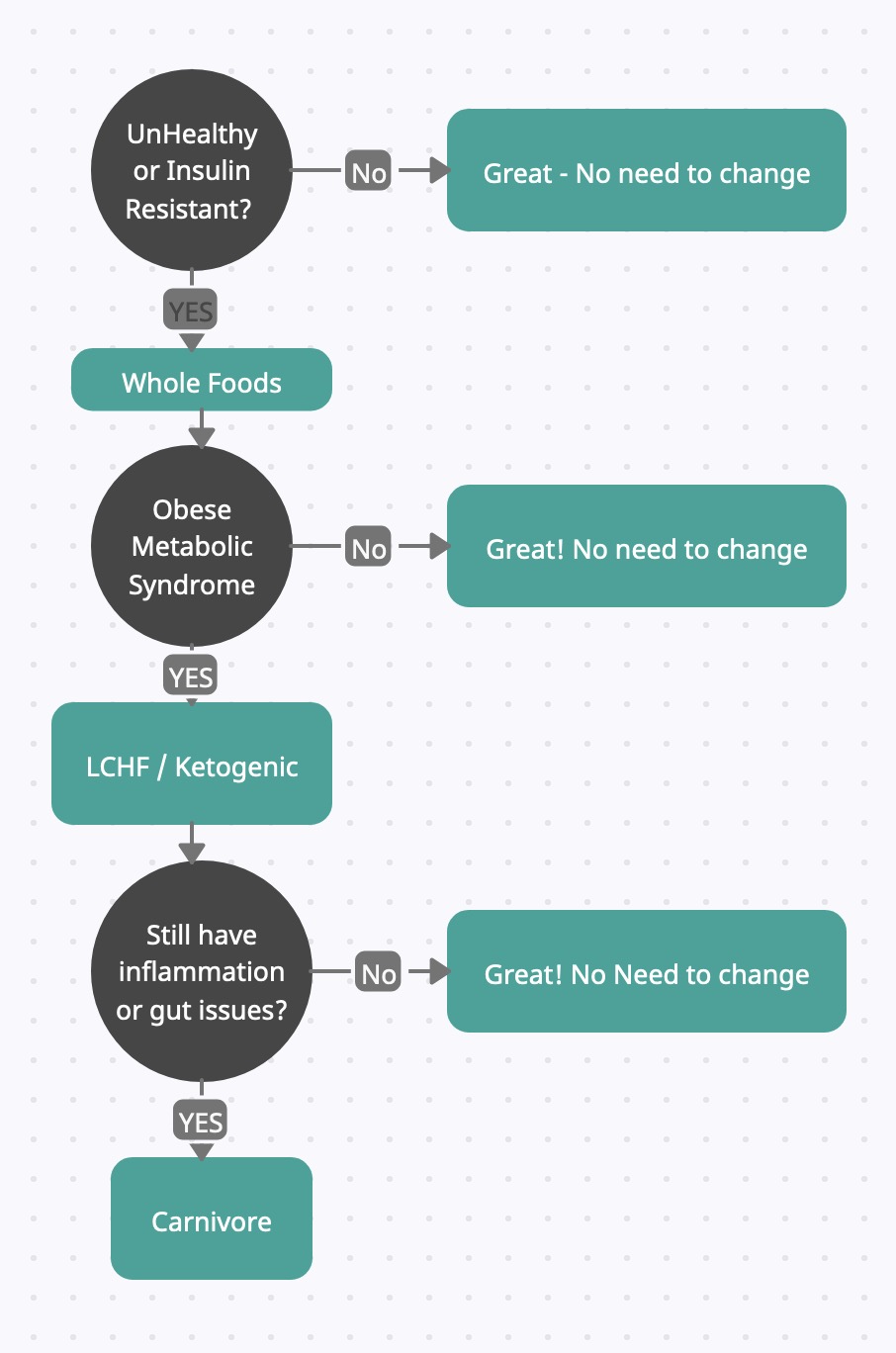
What should you choose?
Ask yourself what you're trying to achieve? What issues are you tackling? The only thing that matters in personal health is your personal outcomes. Focus on what works for you, or is specifically sustainable for you.
Weight Loss - Don't lose weight to get healthy, get healthy to lose weight - A LCHF diet, or even a Whole Food diet, can be used to regain a healthy metabolism
Most of the benefits of Carnivore can be achieved with just LCHF/keto (Even a vegan keto diet). In terms of most effective things you can do, don't worry about carnivore start with LCHF.
If LCHF/Keto isn't enough, such as persistent inflammation, or prolonged gut issues, then Carnivore could be a good option for you.
If you're insulin sensitive, you can keep doing whatever you have been doing - Keep being awesome!
Civility
I'm sure this conversation will touch on people's passions and triggers, I just ask that when you participate you consider the whole human and speak with each other with compassion and empathy for their choices.